Fault Tree Analysis Exam Question
Posted : admin On 04.02.2020Define an event of interest as the TOP event of the faulttreeClearly describe a specific, known event of interest for which you willexplore the potential underlying causes. Events such as the primary eventsand conditions and the secondary events and conditions can be the eventsof interest. Examples might be, 'Flow control valve FCV-1 openedprematurely' or 'The room temperature was greater than 80 ºF.' Typically, the event of interest for a fault tree is an equipment or systemfailure or a human error.When using a fault tree as the primary analysis tool, the accident isthe TOP event.Step 2. Define the next level of the treeDetermine the combinations of events and conditions that can cause theevent to occur. If two or more events must occur to cause the event, usean AND gate and draw the events under the AND gate.
For example, for afire to exist, fuel, an oxygen source, and an ignition sourcemust all occur simultaneously. If there are multiple ways for an eventto occur, use an OR gate. For example, the fuel for a fire can be paperor gasoline.Regardless of whether an AND gate or an OR gate is selected, this levelof development is a 'baby step.'
It should be the smallest logicalstep, within reason, toward the underlying potential causes of the eventabove it. Taking too large a step can cause you to overlook importantpossibilities. Remember to include equipment failures, human errors, andexternal events as appropriate.After the tree level is developed, test the tree for logic. Start witheach event at the bottom of the tree. Does the logic of the tree reflectyour understanding of the event or system? If an event is connected toan OR gate above, then it must be enough to cause the event above.
Ifan event is connected to an AND gate above, is it required to cause theevent above? Must ALL of the other events connected to the AND gate alsooccur for the event above to occur?Step 3. Develop questions to examine the credibility of branchesDevelop questions to test the credibility of each branch. What evidencewould be present if this branch were true?Step 4. Gather data to answer questionsGather data to answer the questions that were generated in the previousstep.Step 5. Use data to determine the credibility of branchesUse the data gathered in the previous step to evaluate which branchesof the tree do or do not contribute to the event of interest.
Do the datasupport or refute the presence of this branch? Do you have sufficientinformation to determine the credibility of the branch?
If not, you needto gather more data or continue on to the next level of the tree. Crossout any branches that you can dismiss with high confidence, and list thespecific data used to make this determination beneath the crossed-outbranch.For chronic problems, assigning probabilities (i.e., percentages) tothe various events will help characterize the types of events that occurmost often. For chronic events, you may not be able to address every typeof event that occurs, so you need to focus on those that occur most frequently.These percentages will be used in Step 6 to determine if we need to developthe event further.If all branches leading to the event of interest through an OR gate orone or more branches leading to the event of interest through an AND gateare eliminated, either (1) the event of interest did not occur, (2) someof the data are inaccurate or were misapplied, or (3) other ways existfor the event of interest to occur.Step 6. Is the branch credible?Determine if the branch is credible. For acute problems, if the branchis credible, continue on to Step 7. If the branch is not credible, proceedto Step 8. For chronic problems, if the percentage of events for thisbranch is high, continue on to Step 7.
If the percentage of events forthis branch is low, proceed to Step 8.Step 7. Is the branch sufficiently developed?Determine if the branch is sufficiently developed. The branch is completewhen it is detailed enough to allow an understanding of how the top eventoccurs.
If the branch is not complete, return to Step 2. If the branchis complete, move on to Step 9.Step 8. Stop branch developmentThere is no reason to develop the branch further if you have determinedit is not credible. Stop development of this branch and move on to Step9.Step 9. Stop when the scenario model is 'complete'The model is complete when you have a clear understanding of how theaccident occurred. Keep your model 'barely adequate' for identifyingthe issues of concern for your analysis; avoid unnecessary detail or resolutionthat will not influence your results. For acute problems, if you havemore than one possible way for the event of interest to have occurredand cannot gather data to dismiss any of the remaining possibilities,you should consider each as a potential causal factor and make recommendationsto prevent each.
For chronic problems, you will typically need to addressa number of primary contributors to the event of interest.Step 10. Identify causal factors (optional)If the fault tree method is being used as the primary analysis tool,causal factors should be identified.Remember, you need not be, and probably will not be, the subject matterexpert for the analysis. Copyright ©2000-2016 Geigle Safety Group, Inc. All rights reserved. Federal copyright prohibits unauthorized reproduction by any means without permission. Students may reproduce materials for personal study. Disclaimer: This material is for training purposes only to inform the reader of occupational safety and health best practices and general compliance requirement and is not a substitute for provisions of the OSH Act of 1970 or any governmental regulatory agency.
CertiSafety is a division of Geigle Safety Group, Inc., and is not connected or affiliated with the U.S. Department of Labor (DOL), or the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
What is Exploratory Testing?Exploratory testing is a hands-on approach in which testers are involved in minimum planning and maximum test execution. The planning involves the creation of a test charter, a short declaration of the scope of a short (1 to 2 hour) time-boxed test effort, the objectives and possible approaches to be used. The test design and test execution activities are performed in parallel typically without formally documenting the test conditions, test cases or test scripts. This does not mean that other, more formal testing techniques will not be used. For example, the tester may decide to use boundary value analysis but will think through and test the most important boundary values without necessarily writing them down. Some notes will be written during the exploratory-testing session so that a report can be produced afterward.2.
What is 'use case testing'?In order to identify and execute the functional requirement of an application from start to finish 'use case' is used and the techniques used to do this is known as 'Use Case Testing.' What is the difference between the STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle) and SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle)?SDLC deals with development/coding of the software while STLC deales with validation and verification of the software4.
What is traceability matrix?The relationship between test cases and requirements is shown with the help of a document. This document is known as a traceability matrix.5. What is Equivalence partitioning testing?Equivalence partitioning testing is a software testing technique which divides the application input test data into each partition at least once of equivalent data from which test cases can be derived. By this testing method, it reduces the time required for software testing.6. What is white box testing and list the types of white box testing?White box testing technique involves selection of test cases based on an analysis of the internal structure (Code coverage, branches coverage, paths coverage, condition coverage, etc.) of a component or system. It is also known as Code-Based testing or Structural testing.
Different types of white box testing are. Statement Coverage. Decision Coverage7. In white box testing, what do you verify?In white box testing following steps are verified. Verify the security holes in the code. Verify the incomplete or broken paths in the code.
Verify the flow of structure according to the document specification. Verify the expected outputs. Verify all conditional loops in the code to check the complete functionality of the application.
Verify the line by line coding and cover 100% testing8. What is black box testing? What are the different black box testing techniques?Black box testing is the software testing method which is used to test the software without knowing the internal structure of code or program. This testing is usually done to check the functionality of an application.
The different black box testing techniques are. Equivalence Partitioning. Boundary value analysis. Cause-effect graphing9.
What is the difference between static and dynamic testing?Static testing: During Static testing method, the code is not executed, and it is performed using the software documentation.Dynamic testing: To perform this testing the code is required to be in an executable form. What are verification and validation?Verification is a process of evaluating software at the development phase. It helps you to decide whether the product of a given application satisfies the specified requirements. Validation is the process of evaluating software at the after the development process and to check whether it meets the customer requirements.11.
What are the different test levels?There are four test levels. Unit/component/program/module testing. Integration testing. System testing. Acceptance testing12. What is Integration testing?is a level of software testing process, where individual units of an application are combined and tested.
It is usually performed after unit and functional testing.13. What Test Plans consists of?Test design, scope, test strategies, approach are various details that Test plan document consists of. Test case identifier. Scope. Features to be tested. Features not to be tested.
Test strategy & Test approach. Test deliverables. Responsibilities. Staffing and training. Risk and Contingencies14. What is the difference between UAT (User Acceptance Testing) and System testing?System Testing: System testing is finding defects when the system undergoes testing as a whole; it is also known as end-to-end testing. In such type of testing, the application suffers from beginning till the end.UAT: User Acceptance Testing (UAT) involves running a product through a series of specific tests which determines whether the product will meet the needs of its users.15.
Mention the difference between Data Driven Testing and Retesting?Retesting: It is a process of checking bugs that are actioned by the development team to verify that they are fixed.Data Driven Testing (DDT): In data driven testing process, the application is tested with multiple test data. The application is tested with a different set of values.16. What are the valuable steps to resolve issues while testing?. Record: Log and handle any problems which have happened.
Report: Report the issues to higher level manager. Control: Define the issue management process17. What is the difference between test scenarios, test cases, and test script?Difference between test scenarios and test cases is thatTest Scenarios: A Test Scenario is any functionality that can be tested. It is also called Test Condition or Test Possibility.Test Cases: It is a document that contains the steps that have to be executed; it has been planned earlier. Test Script: It is written in a programming language and it's a short program used to test part of the functionality of the software system. In other words a written set of steps that should be performed manually.18.
What is Latent defect?Latent defect: This defect is an existing defect in the system which does not cause any failure as the exact set of conditions has never been met19. What are the two parameters which can be useful to know the quality of test execution?To know the quality of test execution, we can use two parameters. Defect reject ratio. Defect leakage ratio20. What is the function of the software testing tool 'phantom'?Phantom is a freeware and is used for windows GUI automation scripting language. It allows us to take control of windows and functions automatically. It can simulate any combination of keystrokes and mouse clicks as well as menus, lists and more.21.
Explain what Test Deliverables is?Test Deliverables are a set of documents, tools and other components that have to be developed and maintained in support of testing.There are different test deliverables at every phase of the software development lifecycle. Before Testing. During Testing. After the Testing22. What is mutation testing?Mutation testing is a technique to identify if a set of test data or test case is useful by intentionally introducing various code changes (bugs) and retesting with original test data/ cases to determine if the bugs are detected.23. What all things you should consider before selecting automation tools for the AUT?. Technical Feasibility.
Complexity level. Application stability. Test data. Application size.
Re-usability of automated scripts. Execution across environment24. How will you conduct Risk Analysis?For the risk analysis following steps need to be implemented.
Finding the score of the risk. Making a profile for the risk. Changing the risk properties. Deploy the resources of that test risk.
Making a database of risk25. What are the categories of debugging?Categories for debugging. Brute force debugging. Backtracking.
Cause elimination. Program Slicing. Fault tree analysis26. What is fault masking explain with example? When the presence of one defect hides.
At that time the presence of another defect in the system is known as fault masking.Example: If the 'Negative Value' cause a firing of unhandled system exception, the developer will prevent the negative values input. This will resolve the issue and hide the defect of unhandled exception firing.27. Explain what Test Plan is? What is the information that should be covered in Test Plan?A test plan can be defined as a document describing the scope, approach, resources, and schedule of testing activities and a test plan should cover the following details. Test Strategy.
Test Objective. Exit/Suspension Criteria. Resource Planning. Test Deliverables28. How can you eliminate the product risk in your project?It helps you to eliminate product risk in your project, and there is a simple yet crucial step that can reduce the product risk in your project.
Investigate the specification documents. Have discussions about the project with all stakeholders including the developer. As a real user walk around the website29. What is the common risk that leads to project failure?The common risk that leads to a project failure are. Not having enough human resource. Testing Environment may not be set up properly.
Limited Budget. Time Limitations30. On what basis you can arrive at an estimation for your project?To estimate your project, you have to consider the following points. Divide the whole project into the smallest tasks. Allocate each task to team members.
Estimate the effort required to complete each task. Validate the estimation31. Explain how you would allocate a task to team members? TaskMember.
Analyze software requirement specification. All the members. Create the test specification.
Tester/Test Analyst. Build up the test environment.
Test administrator. Execute the test cases. Tester, a Test administrator. Report defects. Tester32. Explain what is testing type and what are the commonly used testing type?To get an expected test outcome, a standard procedure is followed which is referred to as Testing Type.Commonly used testing types are.
Unit Testing: Test the smallest code of an application. API Testing: Testing API created for the application. Integration Testing: Individual software modules are combined and tested.
System Testing: Complete testing of the system. Install/UnInstall Testing: Testing done from the point of client/customer view. Agile Testing: Testing through Agile technique33. While monitoring your project what all things you have to consider?The things that have to be taken in considerations are. Is your project on schedule.
Are you over budget. Are you working towards the same career goal. Have you got enough resources. Are there any warning signs of impending problems. Is there any pressure from management to complete the project sooner34. What are the common mistakes which create issues?.
Matching resources to wrong projects. Test manager lack of skills. Not listening to others. Poor Scheduling.
Underestimating. Ignoring the small problems. Not following the process35. What does a typical test report contain? What are the benefits of test reports?A test report contains the following things:. Project Information.
Test Objective. Test Summary. DefectThe benefits of test reports are:. Current status of project and quality of product are informed. If required, stakeholder and customer can take corrective action. A final document helps to decide whether the product is ready for release36. What is test management review and why it is important?Management review is also referred to as Software Quality Assurance or SQA.
SQA focusses more on the software process rather than the software work products. It is a set of activities designed to make sure that the project manager follows the standard process. SQA helps test manager to benchmark the project against the set standards.37. What are the best practices for software quality assurance?The best practices for an effective SQA implementation is. Continuous Improvement. Documentation.
Tool Usage. Metrics. Responsibility by team members. Experienced SQA auditors38.
When is RTM (Requirement Traceability Matrix) prepared?RTM is prepared before test case designing. Requirements should be traceable from review activities.39. What is the difference between Test matrix and Traceability matrix?Test Matrix: Test matrix is used to capture actual quality, effort, the plan, resources and time required to capture all phases of software testingTraceability Matrix: Mapping between test cases and customer requirements is known as Traceability Matrix40. In manual testing what are stubs and drivers?Both stubs and drivers are part of incremental testing. In incremental testing, there are two approaches namely bottom-up and top-down approach. Drivers are used in bottom-up testing and stub is used for a top-down approach.
In order to test the main module, the stub is used, which is a dummy code or program.41. What is the step you would follow once you find the defect?Once a defect is found you would follow the stepa) Recreate the defectb) Attach the screenshotc) Log the defect42. Explain what is 'Test Plan Driven' or 'Key Word Driven' method of testing?This technique uses the actual test case document developed by testers using a spreadsheet containing special 'key Words'. The key words control the processing.43. What is the DFD (Data Flow Diagram)?When a 'flow of data' through an information system is graphically represented, then it is known as Data Flow Diagram. It is also used for the visualization of data processing.44. Explain what LCSAJ is?LCSAJ stands for 'linear code sequence and jump.'
It consists of the following three itemsa) Start of the linear sequence of executable statementsb) End of the linear sequencec) The target line to which control flow is transferred at the end of the linear sequence45. Explain what N+1 testing is?The variation of regression testing is represented as N+1. In this technique, the testing is performed in multiple cycles in which errors found in test cycle 'N' are resolved and re-tested in test cycle N+1. The cycle is repeated unless there are no errors found.46. What is Fuzz testing and when it is used?Fuzz testing is used to detect security loopholes and coding errors in software. In this technique, random data is added to the system in an attempt to crash the system.
If vulnerability persists, a tool called fuzz tester is used to determine potential causes. This technique is more useful for bigger projects but only detects a major fault.47.
Mention what the main advantages of statement coverage metric of software testing are?The benefit of statement coverage metric is thata) It does not require processing source code and can be applied directly to object codeb) Bugs are distributed evenly through the code, due to which percentage of executable statements covered reflects the percentage of faults discovered48. How to generate test cases for 'replace a string' method?a) If characters in new string characters in the previous string. None of the characters should get truncatedb) If characters in new string lengththenbiggestdimension = widthif height widththenbiggestdimension = heightendifelsebiggestdimension = lengthif height lengththenbiggestdimension = heightendifendif479. You have designed test cases to provide 100% statement and 100% decision coverage for the following fragment of code.
If width length then biggestdimension = width else biggestdimension = length endif The following has been added to the bottom of the code fragment above. Print 'Biggest dimension is ' &biggestdimensionprint 'Width: ' & width print 'Length: ' & length How many more test cases are required?None, existing test cases can be used.80. What is the difference between Testing Techniques and Testing Tools?Testing technique: – Is a process for ensuring that some aspects of the application system or unit functions properly there may be few techniques but many tools.Testing Tools: – Is a vehicle for performing a test process.
The tool is a resource to the tester, but itself is insufficient to conduct testingLearn More About Testing Tools81. We use the output of the requirement analysis, the requirement specification as the input for writing User Acceptance Test Cases82. Repeated Testing of an already tested program, after modification, to discover any defects introduced or uncovered as a result of the changes in the software being tested or in another related or unrelated software component:Regression Testing83. A wholesaler sells printer cartridges. The minimum order quantity is 5. There is a 20% discount for orders of 100 or more printer cartridges.
You have been asked to prepare test cases using various values for the number of printer cartridges ordered. Which of the following groups contain three test inputs that would be generated using Boundary Value Analysis?4, 5, 9984.
What is component testing?Component testing, also known as unit, module, and program testing, searches for defects in and verifies the functioning of software (e.g., modules, programs, objects, classes, etc.) that are separately testable. Emergency 4 new york mod. Component testing may be done in isolation from the rest of the system depending on the context of the development life cycle and the system. Most often stubs and drivers are used to replace the missing software and simulate the interface between the software components simply. A stub is called from the software component to be tested; a driver calls a component to be tested.Here is an awesome video on85. What is functional system testing?Testing the end to end functionality of the system as a whole is defined as a functional system testing.86. What are the benefits of Independent Testing?Independent testers are unbiased and identify different defects at the same time.87. In a REACTIVE approach to testing when would you expect the bulk of the test design work to be begun?The bulk of the test design work begun after the software or system has been produced.88.
What are the different Methodologies in Agile Development Model?There are currently seven different agile methodologies that I am aware of:. Extreme Programming (XP). Scrum. Lean Software Development. Feature-Driven Development. Agile Unified Process.
Crystal. Dynamic Systems Development Model (DSDM)89. Which activity in the fundamental test process includes evaluation of the testability of the requirements and system?A 'Test Analysis' and 'Design' includes evaluation of the testability of the requirements and system.90. What is typically the MOST important reason to use risk to drive testing efforts?Because testing everything is not feasible.91. What is random/monkey testing? When is it used?Random testing is often known as monkey testing. In such type of testing data is generated randomly often using a tool or automated mechanism.
With this randomly generated input, the system is tested, and results are analyzed accordingly. These testing are less reliable; hence it is normally used by the beginners and to see whether the system will hold up under adverse effects.92. Which of the following are valid objectives for incident reports?. Provide developers and other parties with feedback about the problem to enable identification, isolation, and correction as necessary. Provide ideas for test process improvement. Provide a vehicle for assessing tester competence. Provide testers with a means of tracking the quality of the system under test.93.
Consider the following techniques. Which are static and which are dynamic techniques?.

Equivalence Partitioning. Use Case Testing. Data Flow Analysis. Exploratory Testing. Decision Testing.
Inspections.Data Flow Analysis and Inspections are static; Equivalence Partitioning, Use Case Testing, Exploratory Testing and Decision Testing are dynamic.94. Why are static testing and dynamic testing described as complementary?Because they share the aim of identifying defects but differ in the types of defect they find.95. What are the phases of a formal review?In contrast to informal reviews, formal reviews follow a formal process. A typical formal review process consists of six main steps:. Planning. Kick-off. Preparation.
Review meeting. Rework. Follow-up.96. What is the role of moderator in the review process?The moderator (or review leader) leads the review process.
He or she determines, in co-operation with the author, the type of review, approach and the composition of the review team. The moderator performs the entry check and the follow-up on the rework, in order to control the quality of the input and output of the review process. The moderator also schedules the meeting, disseminates documents before the meeting, coaches other team members, paces the meeting, leads possible discussions and stores the data that is collected.Learn More about Review process in Video Tutorial97. What is an equivalence partition (also known as an equivalence class)?An input or output ranges of values such that only one value in the range becomes a test case.98.
When should configuration management procedures be implemented?During test planning.99. A Type of Functional Testing, which investigates the functions relating to the detection of threats, such as virus from malicious outsiders?Security Testing100. Testing wherein we subject the target of the test, to varying workloads to measure and evaluate the performance behaviors and the ability of the target and the test to continue to function properly under these different workloads?Load Testing101. Testing activity which is performed to expose defects in the interfaces and in the interaction between integrated components is?Integration Level Testing102.
What are the Structure-based (white-box) testing techniques?Structure-based testing techniques (which are also dynamic rather than static) use the internal structure of the software to derive test cases. They are commonly called 'white-box' or 'glass-box' techniques (implying you can see into the system) since they require knowledge of how the software is implemented, that is, how it works.
For example, a structural technique may be concerned with exercising loops in the software. Different test cases may be derived to exercise the loop once, twice, and many times. This may be done regardless of the functionality of the software.103.
When should 'Regression Testing' be performed?After the software has changed or when the environment has changed should be performed.104. What is negative and positive testing?A negative test is when you put in an invalid input and receives errors. While positive testing is when you put in a valid input and expect some action to be completed in accordance with the specification.105. What is the purpose of a test completion criterion?The purpose of test completion criterion is to determine when to stop testing106.
What can static analysis NOT find?For example memory leaks.107. What is the difference between re-testing and regression testing?Re-testing ensures the original fault has been removed; regression testing looks for unexpected side effects.108.
What are the Experience-based testing techniques?In experience-based techniques, people's knowledge, skills, and background are a prime contributor to the test conditions and test cases. The experience of both technical and business people is important, as they bring different perspectives to the test analysis and design process. Due to previous experience with similar systems, they may have insights into what could go wrong, which is very useful for testing.109. What type of review requires formal entry and exit criteria, including metrics?Inspection110.
Could reviews or inspections be considered part of testing?Yes, because both help detects faults and improves quality.111. An input field takes the year of birth between 1900 and 2004 what the boundary values for testing this field are?1899,1900,20. Which of the following tools would be involved in the automation of regression test? Data tester b. Boundary tester c. Capture/Playback d. Output comparator.d.
Output comparator113. To test a function, what has to write a programmer, which calls the function to be tested and pass test data.Driver114. What is the one Key reason why developers have difficulty testing their own work?Lack of Objectivity115.' How much testing is enough?'
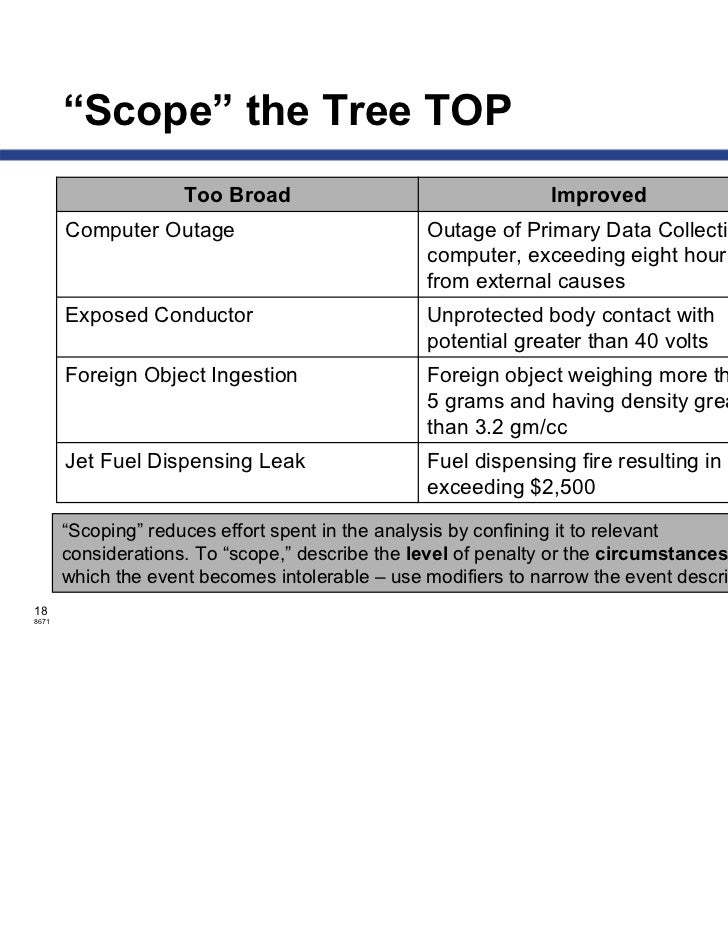
History Of Fault Tree Analysis
The answer depends on the risk for your industry, contract and special requirements.116. When should testing be stopped?It depends on the risks for the system being tested. There are some criteria based on which you can stop testing. Deadlines (Testing, Release). Test budget has been depleted.
Bug rate fall below a certain level. Test cases completed with certain percentage passed. Alpha or beta periods for testing ends.
Coverage of code, functionality or requirements are met to a specified point117. Which of the following is the primary purpose of the integration strategy for integration testing in the small?The primary purpose of the integration strategy is to specify which modules to combine when and how many at once.118.
What are semi-random test cases?Semi-random test cases are nothing, but when we perform random test cases and do equivalence partitioning to those test cases, it removes redundant test cases, thus giving us semi-random test cases.119. Given the following code, which statement is true about the minimum number of test cases required for full statement and branch coverage?Read pRead qIF p+q 100THEN Print 'Large'ENDIFIF p 50THEN Print 'p Large'ENDIF1 test for statement coverage, 2 for branch coverage120. Which review is normally used to evaluate a product to determine its suitability for the intended use and to identify discrepancies?Technical Review.121. Faults found should be originally documented by whom?By testers.122. Which is the current formal world-wide recognized documentation standard?There isn't one.123. Which of the following is the review participant who has created the item to be reviewed?Author124. A number of critical bugs are fixed in software.
All the bugs are in one module, related to reports. The test manager decides to do regression testing only on the reports module.Regression testing should be done on other modules as well because fixing one module may affect other modules.125. Why does the boundary value analysis provide good test cases?Because errors are frequently made during programming of the different cases near the 'edges' of the range of values.126. What makes an inspection different from other review types?It is led by a trained leader, uses formal entry and exit criteria and checklists.127. Why can be tester dependent on configuration management?Because configuration management assures that we know the exact version of the testware and the test object.128.
What is V-Model?A software development model that illustrates how testing activities integrate with software development phases129. What is maintenance testing?Triggered by modifications, migration or retirement of existing software130. What is test coverage?Test coverage measures in some specific way the amount of testing performed by a set of tests (derived in some other way, e.g., using specification-based techniques). Wherever we can count things and can tell whether or not each of those things has been tested by some test, then we can measure coverage.131. Why is incremental integration preferred over 'big bang' integration?Because incremental integration has better early defects screening and isolation ability132. What is called the process starting with the terminal modules?Bottom-up integration133.
During which test activity could fault be found most cost-effectively?During test planning134. The purpose of the requirement phase isTo freeze requirements, to understand user needs, to define the scope of testing135. Why we split testing into distinct stages?We split testing into distinct stages because of the following reasons,. Each test stage has a different purpose. It is easier to manage to test in stages. We can run different test into different environments. Performance and quality of the testing is improved using phased testing136.
What is DRE?In order to measure test effectiveness, a powerful metric is used to measure test effectiveness known as DRE (Defect Removal Efficiency) From this metric we would know how many bugs we have found from the set of test cases. The formula for calculating DRE isDRE=Number of bugs while a testing/number of bugs while testing + number of bugs found by a user137. Which of the following is likely to benefit most from the use of test tools providing test capture and replay facilities?
A) Regression testing b) Integration testing c) System testing d) User acceptance testingRegression testing138. How would you estimate the amount of re-testing likely to be required?Metrics from previous similar projects and discussions with the development team139. What studies data flow analysis?The use of data on paths through the code.140. What is failure?Failure is a departure from specified behavior.141.
Advantages Of Fault Tree Analysis
What are Test comparators?Is it really a test if you put some inputs into some software, but never look to see whether the software produces the correct result? The essence of testing is to check whether the software produces the correct result and to do that, and we must compare what the software produces to what it should produce. A test comparator helps to automate aspects of that comparison.142. Who is responsible for document all the issues, problems and open point that were identified during the review meetingScribe143. What is the main purpose of Informal reviewAn inexpensive way to get some benefit144.
Exam Question Analysis
What is the purpose of test design technique?Identifying test conditions and Identifying test cases145. When testing a grade calculation system, a tester determines that all scores from 90 to 100 will yield a grade of A, but scores below 90 will not. This analysis is known as:Equivalence partitioning146. A test manager wants to use the resources available for the automated testing of a web application.
The best choice is Tester, test automation, web specialist, DBA147. During the testing of a module tester, 'X' found a bug and assigned it to a developer. But developer rejects the same, saying that it's not a bug. What 'X' should do?Send the detailed information of the bug encountered and check the reproducibility148. A type of integration testing in which software elements, hardware elements, or both are combined all at once into a component or an overall system, rather than in stages.Big-Bang Testing149.
In practice, which Life Cycle model may have more, fewer or different levels of development and testing, depending on the project and the software product. For example, there may be component integration testing after component testing, and system integration testing after system testing.V-Model150. Which technique can be used to achieve input and output coverage?
It can be applied to human input, input via interfaces to a system, or interface parameters in integration testing.Equivalence partitioning151. 'This life cycle model is driven by schedule and budget risks' This statement is best suited for.V-Model152. In which order should tests be run?The most important one must be tested first153.
The later in the development life cycle a fault is discovered, the more expensive it is to fix. Why?The fault has been built into more documentation, code, tests, etc154. What is Coverage measurement?It is a partial measure of test thoroughness.155.
What is Boundary value testing?Test boundary conditions on, below and above the edges of input and output equivalence classes. For instance, let say a bank application where you can withdraw maximum Rs.20,000 and a minimum of Rs.100, so in boundary value testing we test only the exact boundaries, rather than hitting in the middle. That means we test above the maximum limit and below the minimum limit.156. What does COTS represent?Commercial Off The Shelf.157.The purpose of which is to allow specific tests to be carried out on a system or network that resembles as closely as possible the environment where the item under test will be used upon release?Test Environment158. What can be thought of as being based on the project plan, but with greater amounts of detail?Phase Test Plan159. What is Rapid Application Development?Rapid Application Development (RAD) is formally a parallel development of functions and subsequent integration. Components/functions are developed in parallel as if they were mini projects, the developments are time-boxed, delivered, and then assembled into a working prototype.
This can very quickly give the customer something to see and use and to provide feedback regarding the delivery and their requirements. Rapid change and development of the product are possible using this methodology. However the product specification will need to be developed for the product at some point, and the project will need to be placed under more formal controls before going into production.Refer Our.